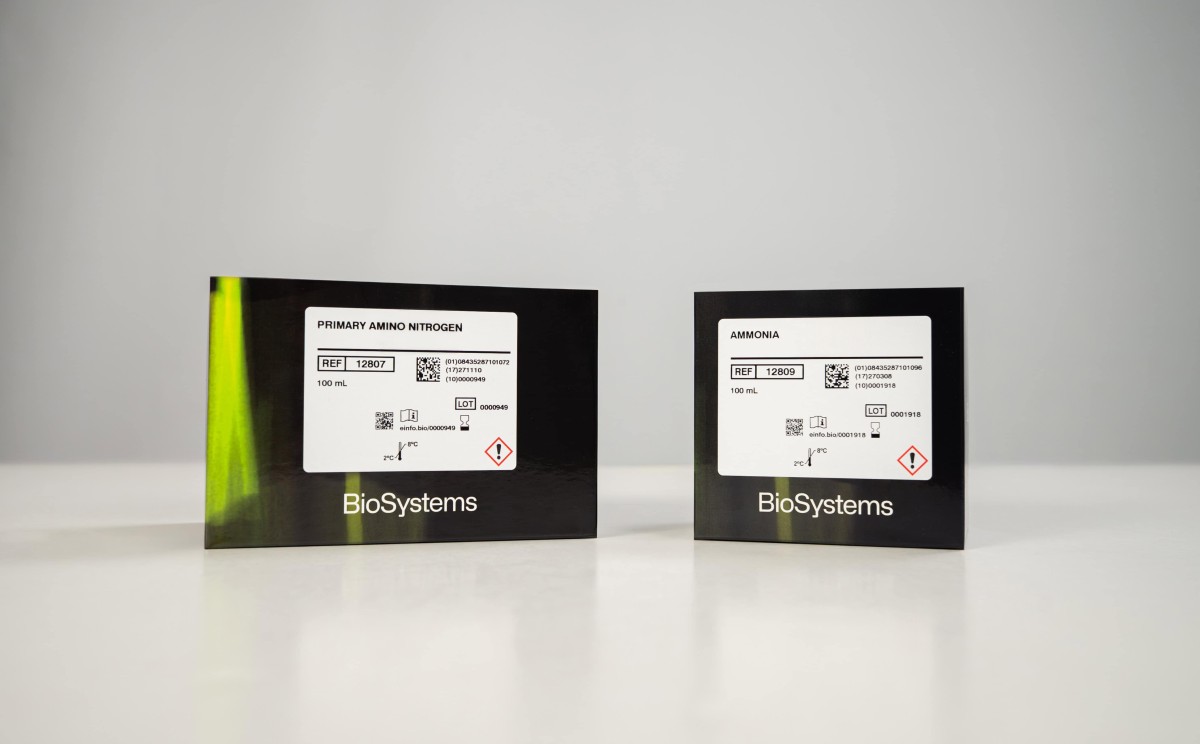
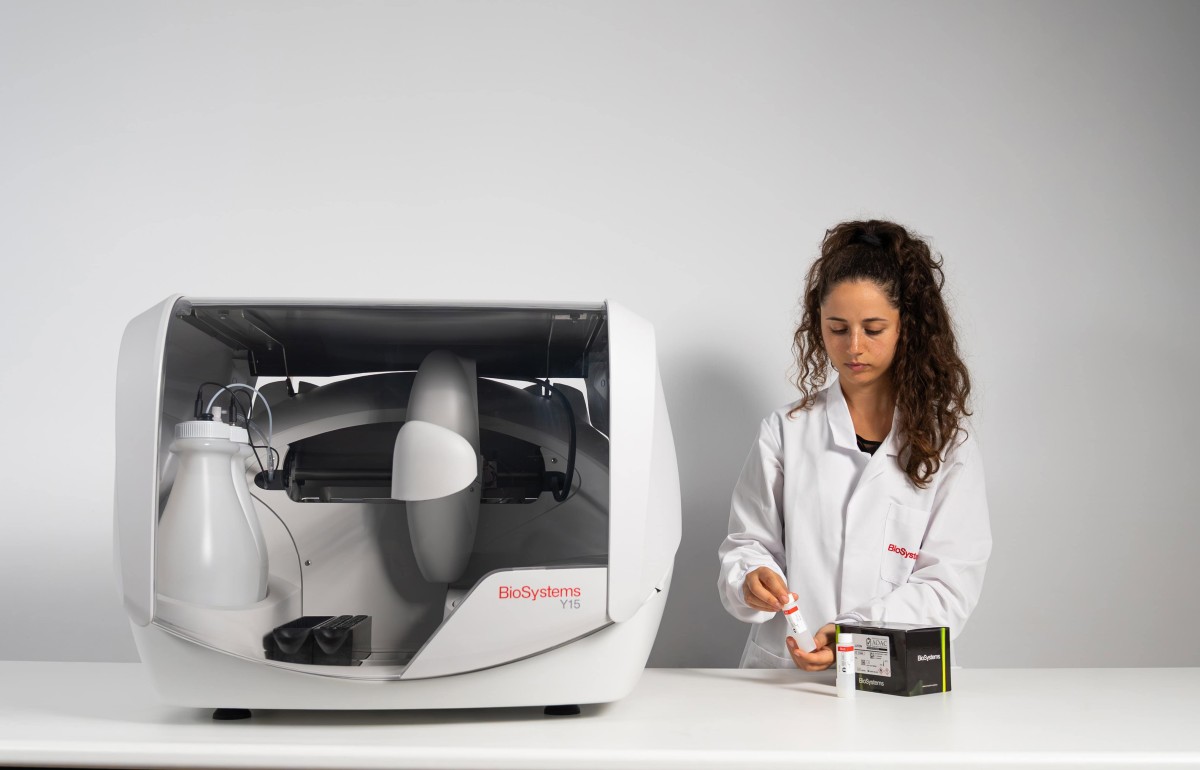
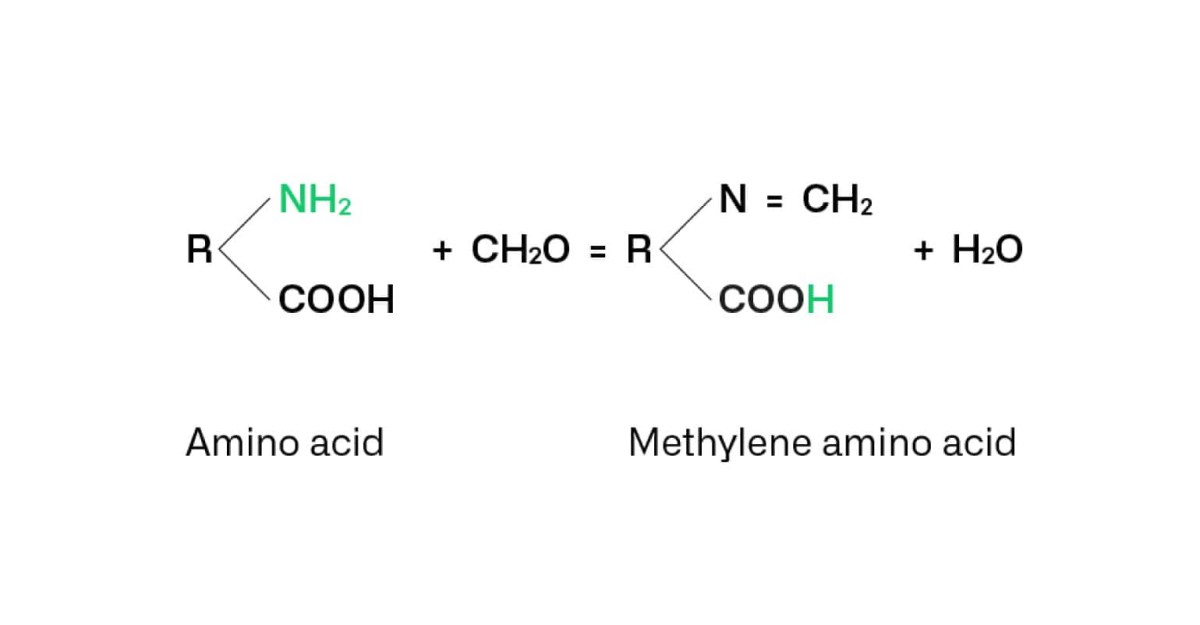
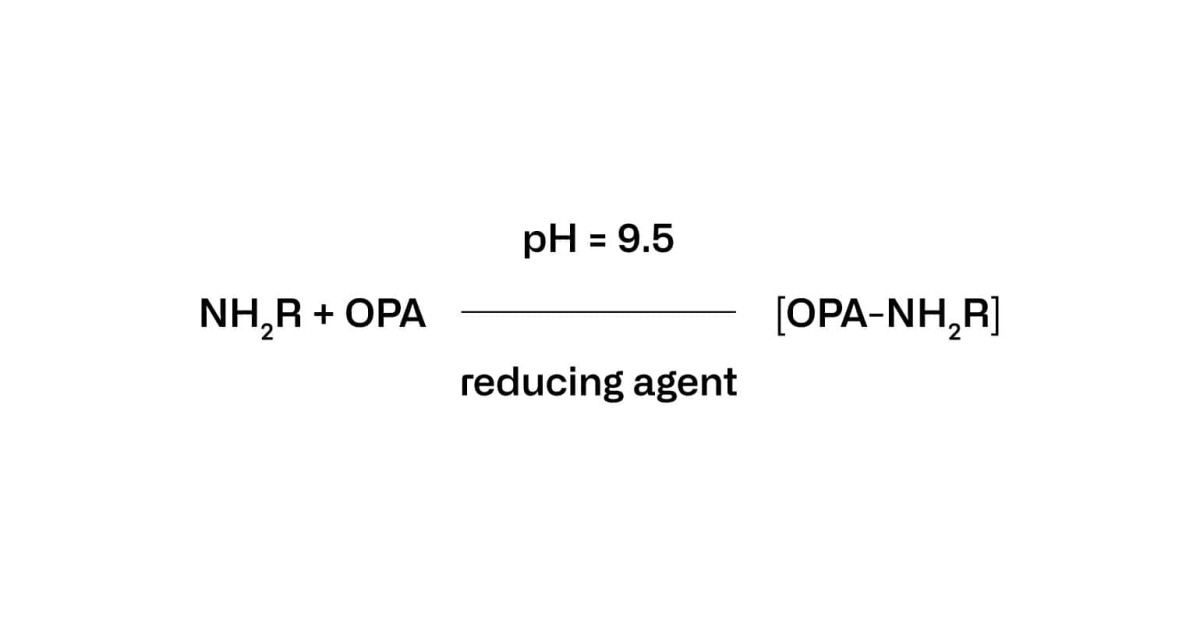
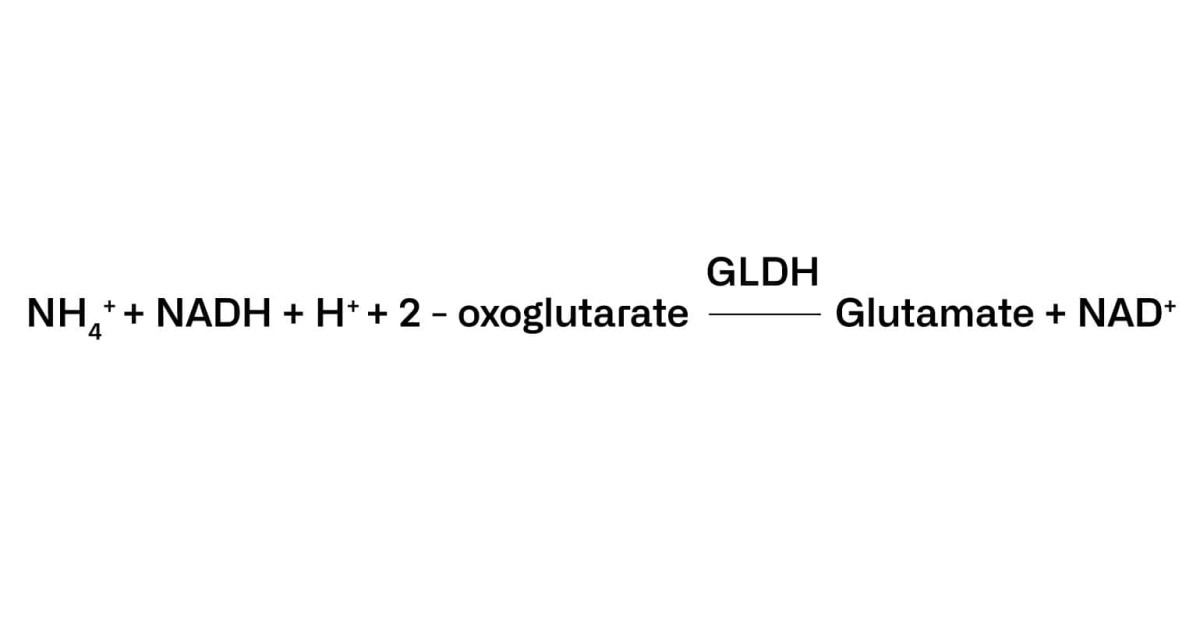
Formol Number, also known as Formol Index, measures the content of Primary Amino Nitrogen (PAN) from free amino acids and ammonium present in a sample. It is used as a quality parameter of fruit juice, grape must and wine.
- About
- Solutions
-
Clinical Analysis
-
Biochemistry Systems
-
If you are interested in our solutions for Clinical Analysis, you can learn more on our Global website and reach out to us with your needs. Visit our Global Website
-
Autoimmunity Systems
-
If you are interested in our solutions for Clinical Analysis, you can learn more on our Global website and reach out to us with your needs. Visit our Global Website
-
-
Veterinary Analysis
-
Biochemistry Systems
-
If you are interested in our solutions for Clinical Analysis, you can learn more on our Global website and reach out to us with your needs. Visit our Global Website
-
Vector-borne Diseases Systems
-
If you are interested in our solutions for Clinical Analysis, you can learn more on our Global website and reach out to us with your needs. Visit our Global Website
-
-
Food & Beverage Analysis
-
Environmental Analysis
-
Bioprocess Analysis
-
- Discover
- Contact
- Resources

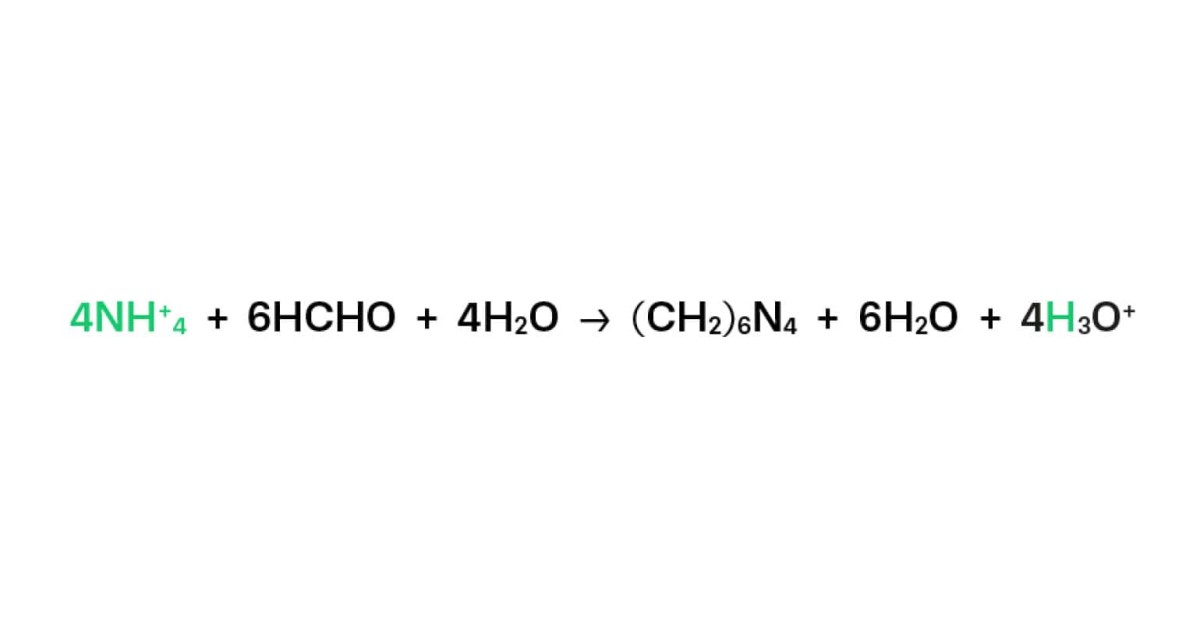



1.thigh.jpg)